Step into the world of Birth Control for Women where knowledge meets empowerment, guiding you through a journey of informed decisions and well-being.
Discover the array of contraceptive options, from hormonal to non-hormonal methods, tailored to women’s unique needs and preferences.
Introduction to Birth Control for Women
Birth control, also known as contraception, plays a crucial role in women’s reproductive health by allowing them to plan and space their pregnancies. It involves various methods that help prevent pregnancy by either blocking sperm from reaching the egg, stopping ovulation, or altering the lining of the uterus.
Types of Birth Control Methods
There are several types of birth control methods available for women, each with its own advantages and considerations:
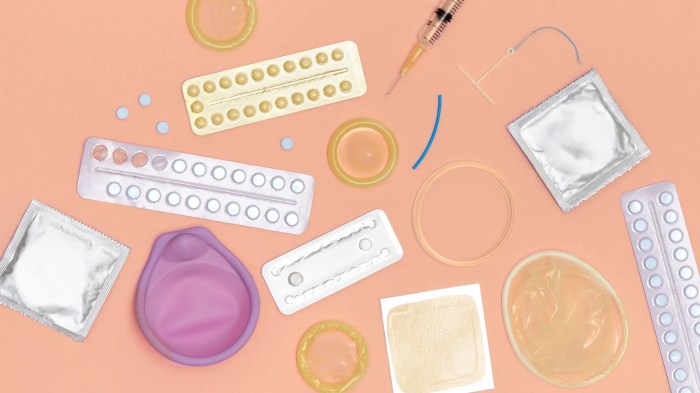
- Barrier Methods: such as condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps, physically block sperm from reaching the egg.
- Hormonal Methods: including birth control pills, patches, injections, and implants, work by altering hormone levels to prevent ovulation.
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): small T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus to prevent fertilization or implantation of the egg.
- Sterilization: permanent methods like tubal ligation or hysterectomy for women who do not wish to have more children.
Benefits of Using Birth Control
Using birth control offers numerous benefits for women’s overall well-being:
- Allows women to plan pregnancies according to their life goals and circumstances.
- Helps regulate menstrual cycles, reduce menstrual cramps, and manage hormonal imbalances.
- Can improve acne, reduce the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers, and manage conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Provides greater control over reproductive choices, empowering women to make informed decisions about their bodies and futures.
Types of Contraceptives
Contraceptives are essential tools for women to prevent unwanted pregnancies and take control of their reproductive health. There are various types of contraceptives available, including hormonal and non-hormonal options, each with its own set of benefits and considerations.
Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives work by altering a woman’s hormone levels to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus to block sperm, or thin the uterine lining to prevent implantation. These include birth control pills, patches, injections, vaginal rings, and hormonal IUDs. They are highly effective when used correctly, with a success rate of over 90%.
Non-Hormonal Contraceptives
Non-hormonal contraceptives provide birth control without affecting a woman’s hormone levels. Options include barrier methods like condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps, as well as copper IUDs. While non-hormonal contraceptives may have fewer side effects for some women, they are generally less effective than hormonal methods, with success rates ranging from 70% to 85%.
Effectiveness Rates
When it comes to preventing pregnancy, the effectiveness of contraceptives varies. Hormonal methods like birth control pills are more than 99% effective with perfect use, while non-hormonal methods like condoms have a lower success rate of around 85%. It’s important for women to choose a contraceptive method that aligns with their lifestyle and preferences to ensure optimal protection against unintended pregnancies.
Hormonal Birth Control Methods
When it comes to regulating women’s fertility, hormonal birth control methods play a vital role. These methods work by altering hormone levels in the body to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus to block sperm, and thin the uterine lining to inhibit implantation of a fertilized egg.
Popular Hormonal Contraceptives
There are several popular hormonal contraceptives available to women, each offering different benefits and considerations:
- Birth Control Pills: These are taken daily and contain synthetic hormones to prevent pregnancy. They are highly effective when taken correctly but may have side effects such as nausea, weight gain, and mood changes.
- Birth Control Patches: These patches are worn on the skin and release hormones into the bloodstream to prevent ovulation. They are convenient but may cause skin irritation at the application site.
- Hormonal IUDs: Intrauterine devices releasing hormones are implanted in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. They are long-lasting and reversible but may cause side effects like irregular bleeding and cramping.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While hormonal birth control methods are highly effective, they also come with potential side effects and risks to consider:
- Common Side Effects: These may include nausea, headaches, breast tenderness, and mood changes. These usually subside after a few months as the body adjusts to the hormones.
- Rare but Serious Risks: There is a slight increased risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart attack with hormonal contraceptives, especially for women who smoke or have certain health conditions.
- Impact on Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal birth control can also affect the regularity and intensity of menstrual periods, leading to lighter or absent periods in some women.
Non-Hormonal Birth Control Methods
Non-hormonal birth control methods offer women hormone-free options to prevent pregnancy. These methods are often preferred by individuals who may have concerns about hormonal birth control.
Copper IUDs
Copper Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) are small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. The copper on the IUD creates an inflammatory response in the uterus, which is toxic to sperm and eggs, thus preventing fertilization.
Barrier Methods
Barrier methods such as condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps physically block sperm from reaching the egg. These methods are non-hormonal and can be used as needed.
Fertility Awareness Methods
Fertility awareness methods involve tracking menstrual cycles and ovulation to identify fertile days and avoid unprotected sex during those times. This method requires diligence and consistency but can be effective when used correctly.
Reproductive Health and Birth Control

Reproductive health plays a crucial role in women’s overall well-being, and access to birth control methods is a key component of reproductive healthcare.
The Relationship Between Reproductive Health and Birth Control
- Birth control methods help women to plan and space pregnancies, which can positively impact their physical, emotional, and socioeconomic health.
- By preventing unintended pregnancies, birth control contributes to reducing maternal mortality rates and promoting safer childbirth practices.
- Regular use of contraceptives can also help in managing certain reproductive health conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis.
Access to Birth Control and Women’s Reproductive Rights
- Access to a range of birth control options empowers women to make informed choices about their reproductive futures.
- By having control over if and when to have children, women can pursue education, career goals, and personal aspirations without the constraints of unplanned pregnancies.
- Ensuring universal access to birth control is essential for upholding women’s reproductive rights and promoting gender equality.
Role of Healthcare Providers in Educating Women
- Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating women about the various birth control methods available and helping them choose the most suitable option based on their individual needs and preferences.
- Through comprehensive counseling and guidance, healthcare providers can address any concerns or misconceptions women may have about birth control, ensuring they make informed decisions.
- Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare providers also enable women to monitor their reproductive health and make any necessary adjustments to their birth control method.
Final Review

Empower yourself with the understanding of reproductive health and birth control, paving the way for informed choices and enhanced well-being.
FAQ Guide
Are there natural alternatives to hormonal birth control?
Yes, options like fertility awareness methods and barrier methods provide hormone-free alternatives.
Can birth control methods protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
No, contraceptives only prevent pregnancy, not STIs. It’s advisable to use condoms for STI prevention.
Do all hormonal birth control methods have the same side effects?
No, side effects can vary depending on the method. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.