Delve into the intricate world of birth control as we unravel the mechanisms behind its effectiveness, shedding light on the various methods that empower individuals in their reproductive health choices.
From hormonal contraceptives to barrier methods, this topic is a crucial aspect of reproductive health that influences lives in profound ways.
How Does Birth Control Work?
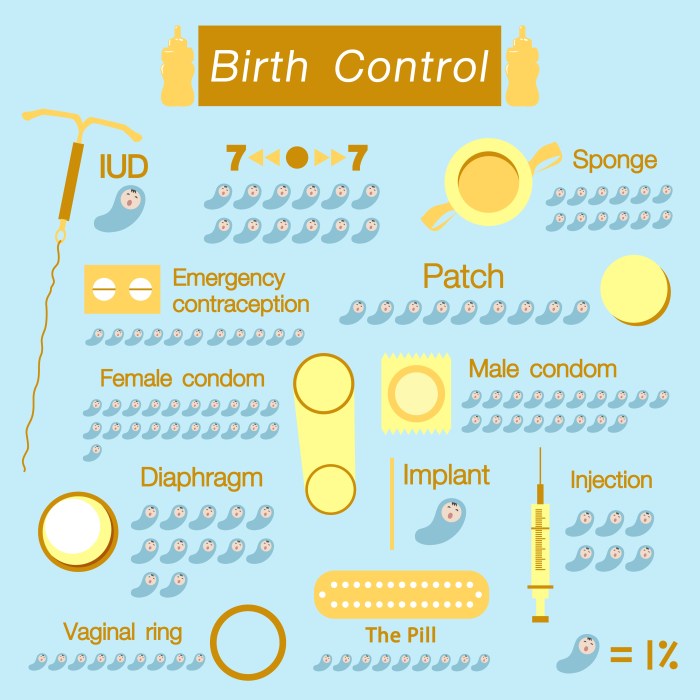
Birth control methods are designed to prevent pregnancy by either inhibiting ovulation, fertilization, or implantation of a fertilized egg. There are various types of birth control methods, each with its unique mechanism of action.
Types of Birth Control Methods
- Hormonal contraceptives: These methods contain synthetic hormones like estrogen and progestin, which prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus to hinder sperm movement.
- Barrier methods: Condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps physically block sperm from reaching the egg.
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs): These T-shaped devices are inserted into the uterus to prevent fertilization or implantation.
- Sterilization: Permanent methods like tubal ligation or vasectomy block fallopian tubes or vas deferens to prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
Mechanism of Action for Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives work by primarily preventing ovulation, which inhibits the release of an egg for fertilization. They also thicken cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may alter the uterine lining, making it less receptive to a fertilized egg.
Role of Barrier Methods in Preventing Pregnancy
Barrier methods create a physical barrier between sperm and the egg, preventing fertilization. Condoms, for example, not only provide protection against pregnancy but also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Fertility Awareness Methods
Fertility awareness methods involve tracking changes in a woman’s body to determine fertile days and avoid unprotected intercourse during that time. This may include monitoring basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and menstrual cycles to predict ovulation.
Understanding Contraceptives and Birth Control
Contraceptives play a crucial role in reproductive health by allowing individuals to prevent unwanted pregnancies and plan their families effectively. By understanding the different forms of birth control available, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
Types of Birth Control
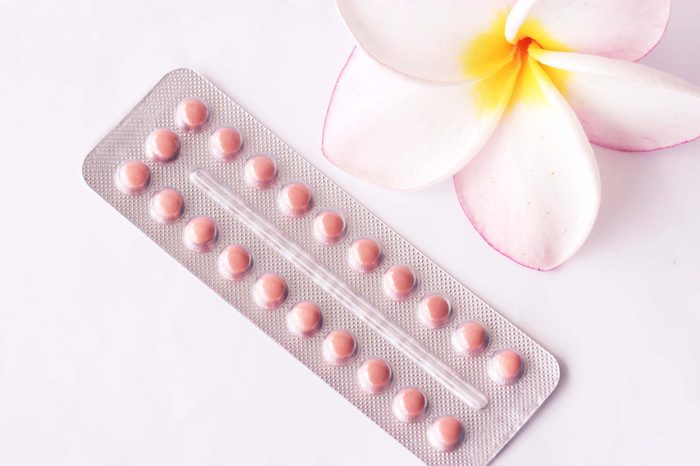
- Pills: Oral contraceptives are taken daily and contain hormones to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
- Patches: Transdermal patches release hormones through the skin to prevent ovulation and alter the uterine lining to inhibit implantation of fertilized eggs.
- Injections: Depo-Provera injections are administered every three months and contain progestin to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus.
- Implants: Small rods inserted under the skin release hormones to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus, providing long-term contraception.
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception, also known as the “morning-after pill,” consists of high doses of hormones that prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse. It works by delaying or inhibiting ovulation, fertilization, or implantation of a fertilized egg.
Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARCs)
- IUDs: Intrauterine devices are small T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. They can be hormonal or non-hormonal and offer long-term contraception with high effectiveness rates.
- Implants: Contraceptive implants are small rods inserted under the skin that release hormones to prevent ovulation. They provide up to 3-5 years of contraception with high efficacy.
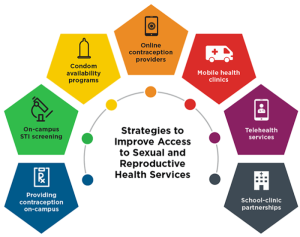
Reproductive Health and Birth Control

Reproductive health education plays a crucial role in empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual and reproductive well-being. It encompasses a range of topics such as contraception, family planning, sexually transmitted infections, and pregnancy care.
Significance of Reproductive Health Education
- Empowers individuals to make informed choices regarding their reproductive health.
- Reduces the risk of unplanned pregnancies and sexually transmitted infections.
- Promotes gender equality by ensuring equal access to reproductive health information and services.
- Helps individuals understand their bodies and reproductive rights.
Impact of Access to Birth Control on Reproductive Rights
- Access to birth control allows individuals to plan if, when, and how many children they want to have.
- Empowers individuals to make decisions about their reproductive health without external interference.
- Ensures that individuals have the right to control their fertility and make choices that align with their life goals.
- Contributes to overall reproductive autonomy and bodily integrity.
Importance of Family Planning Services in Promoting Reproductive Health
- Family planning services offer a range of contraceptive methods to help individuals prevent unintended pregnancies.
- Enable individuals to space pregnancies and plan for the future.
- Provide counseling and support to individuals in making decisions about their reproductive health.
- Reduce maternal and infant mortality rates by promoting healthy spacing of pregnancies.
Relationship Between Birth Control Options and Gender Equality
- Access to a variety of birth control options gives individuals the freedom to choose a method that best suits their needs and preferences.
- Promotes gender equality by allowing both men and women to take an active role in family planning.
- Reduces the burden of contraception primarily falling on women and empowers men to participate in reproductive decision-making.
- Contributes to breaking down traditional gender roles and promoting equal responsibility for reproductive health.
Final Summary
As we conclude our exploration of How Does Birth Control Work?, we are reminded of the pivotal role it plays in shaping reproductive rights, gender equality, and overall well-being.
FAQ Insights
How does the contraceptive pill work?
The contraceptive pill works by preventing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and altering the uterine lining to inhibit fertilization and implantation.
Are hormonal contraceptives safe to use?
Hormonal contraceptives are generally safe for most women, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best option based on individual health needs.
Do barrier methods like condoms protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
Yes, barrier methods like condoms provide protection not only against pregnancy but also against STIs when used consistently and correctly.
How effective are long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) compared to other methods?
LARCs, such as IUDs and implants, are highly effective with a lower failure rate compared to other methods like the pill or condoms.
What role does fertility awareness play in birth control?
Fertility awareness methods involve tracking menstrual cycles and ovulation to identify fertile days, allowing individuals to avoid unprotected intercourse during those times to prevent pregnancy.