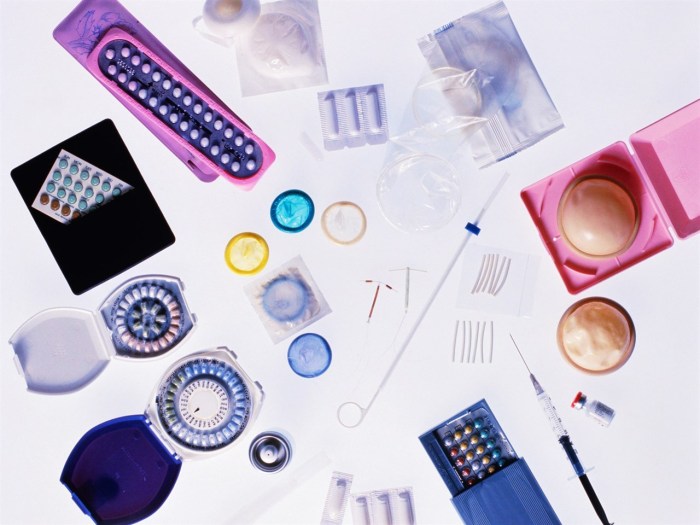
Embark on a journey through the realm of contraceptives, exploring the diverse array of options available to individuals seeking to take charge of their reproductive health. From hormonal methods to barrier techniques, the world of contraception is vast and varied, offering solutions tailored to different needs and preferences.
Delve deeper into the nuances of each contraceptive type to gain a comprehensive understanding of how they function and their efficacy in preventing pregnancy.
Types of Contraceptives
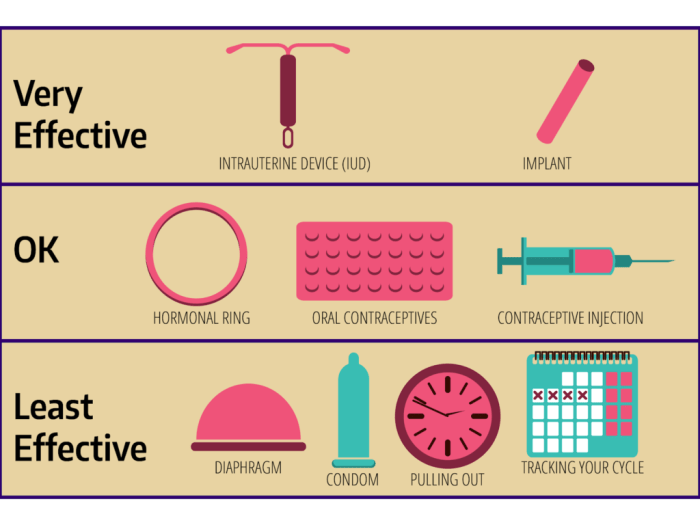
Contraceptives are essential tools for individuals who wish to prevent unwanted pregnancies. There are various types of contraceptives available, each falling into distinct categories based on their mechanisms of action.
Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives work by altering hormone levels in the body to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin the lining of the uterus. They include:
- Birth control pills
- Birth control patches
Barrier Contraceptives
Barrier contraceptives physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg. They include:
- Condoms (male and female)
- Diaphragms
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
IUDs are small T-shaped devices placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. They can be hormonal or non-hormonal and include:
- Copper IUDs
Sterilization
Sterilization procedures permanently prevent pregnancy by blocking the fallopian tubes in women or the vas deferens in men. They include:
- Vasectomy (male sterilization)
- Tubal ligation (female sterilization)
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable contraceptive method based on individual needs and health considerations.
Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives are a type of birth control method that contains synthetic hormones. They are available in various forms such as birth control pills, patches, injections, and implants.
These contraceptives work by regulating the menstrual cycle and preventing ovulation. They contain hormones like estrogen and progestin that inhibit the release of an egg from the ovaries, making it difficult for sperm to fertilize the egg.
Benefits and Potential Side Effects
- Hormonal contraceptives are highly effective in preventing pregnancy when used correctly.
- They can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce menstrual cramps, and make periods lighter and more predictable.
- Some types of hormonal contraceptives have non-contraceptive benefits such as reducing acne and protecting against certain cancers.
However, there are potential side effects associated with hormonal contraceptives, including:
- Nausea, bloating, breast tenderness, or mood changes
- Irregular bleeding or spotting
- Headaches or migraines
- Increased risk of blood clots, especially in women who smoke or have other risk factors
Barrier Methods
Contraceptive barrier methods work by creating a physical barrier to prevent sperm from reaching the egg during sexual intercourse. These methods are often used to prevent pregnancy and reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Types of Barrier Methods
- Condoms: Condoms are thin sheaths worn on the penis (male condoms) or inserted into the vagina (female condoms) to collect semen and prevent it from entering the vagina.
- Diaphragms: Diaphragms are shallow, dome-shaped silicone devices that cover the cervix and block sperm from entering the uterus.
- Cervical Caps: Cervical caps are smaller than diaphragms and are designed to fit snugly over the cervix to prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
- Contraceptive Sponges: Contraceptive sponges are soft, disposable devices that are soaked in spermicide and inserted into the vagina to block and kill sperm.
These barrier methods are user-dependent and must be used correctly and consistently to be effective.
Effectiveness of Barrier Methods
- Condoms: Male condoms are about 85% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use, while female condoms are around 79% effective. Both types of condoms also provide some protection against STIs.
- Diaphragms and Cervical Caps: Diaphragms and cervical caps are 71-88% effective in preventing pregnancy and do not provide protection against STIs. They must be used with spermicide for maximum effectiveness.
- Contraceptive Sponges: Contraceptive sponges are approximately 76-88% effective in preventing pregnancy and may offer some protection against STIs due to the inclusion of spermicide.
How Barrier Methods Work
Barrier methods like condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and contraceptive sponges physically block sperm from reaching the egg by creating a barrier at the cervix or inside the vagina. This barrier prevents sperm from entering the uterus and fertilizing an egg, thus preventing pregnancy.
Sterilization
Sterilization is a permanent form of contraception that involves surgical procedures to prevent pregnancy. It is considered a highly effective method for individuals who have decided not to have children or do not wish to have any more children.
Vasectomy for Males
Vasectomy is a surgical procedure for males that involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles. This prevents sperm from mixing with semen, making a man sterile and unable to father a child. It is a relatively simple and quick procedure that can be done in a doctor’s office.
Tubal Ligation for Females
Tubal ligation, also known as “getting your tubes tied,” is a surgical procedure for females that involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes. This prevents eggs from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus, making a woman sterile and unable to conceive. It is a more invasive procedure compared to vasectomy and is usually performed in a hospital under general anesthesia.
Considerations, Benefits, and Risks
- Sterilization is considered a permanent form of contraception and is not easily reversible. Individuals must be certain about their decision before undergoing the procedure.
- Benefits of sterilization include long-term effectiveness, convenience, and cost-effectiveness compared to other contraceptive methods over time.
- Potential risks associated with sterilization include surgical complications, such as infection or bleeding, as well as the rare possibility of a failed procedure leading to an unintended pregnancy.
Contraceptives, Birth Control, Reproductive Health

Contraceptives play a crucial role in family planning and reproductive health by providing individuals with the ability to make informed decisions about their reproductive choices. Access to contraceptives empowers individuals to take control of their own bodies and plan for their futures.
Importance of Contraceptives in Family Planning
Contraceptives are essential in preventing unintended pregnancies, allowing individuals to have the number of children they desire and at the time that is right for them. By effectively spacing out pregnancies, contraceptives can also help reduce maternal mortality rates and improve overall maternal and child health.
Empowerment Through Contraceptive Access
Access to contraceptives not only empowers individuals to make decisions about their reproductive health but also gives them the freedom to pursue education, careers, and personal goals without the interruption of unplanned pregnancies. This empowerment is key in promoting gender equality and women’s rights.
Role of Contraceptives in Preventing Unintended Pregnancies
Contraceptives are highly effective in preventing unintended pregnancies, which can have significant social, economic, and health implications. By reducing the number of unplanned pregnancies, contraceptives contribute to healthier families and communities, ultimately promoting overall well-being.
Epilogue
As we conclude our exploration of contraceptives, one thing remains clear: the significance of these methods in empowering individuals to make informed choices about their reproductive well-being cannot be overstated. By shedding light on the various options available, we pave the way for a future where everyone has access to safe and effective means of family planning.
Questions and Answers
How do hormonal contraceptives regulate the menstrual cycle?
Hormonal contraceptives work by suppressing ovulation and altering the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
What are the benefits of using barrier methods?
Barrier methods not only prevent pregnancy but also serve as a protective measure against sexually transmitted infections.
Are intrauterine devices (IUDs) suitable for everyone?
IUDs are generally safe for most individuals, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best option based on individual health factors.
How do sterilization procedures like vasectomy and tubal ligation work?
Vasectomy involves blocking the vas deferens to prevent sperm from mixing with semen, while tubal ligation blocks or seals the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from reaching the uterus.
What role do contraceptives play in promoting overall well-being?
Contraceptives not only prevent unintended pregnancies but also contribute to reducing maternal mortality rates and empowering individuals to make informed reproductive choices.